Ballista 分布式查询引擎 - 计划执行
2024-04-27
所有计划的执行均由 Executor 节点负责。
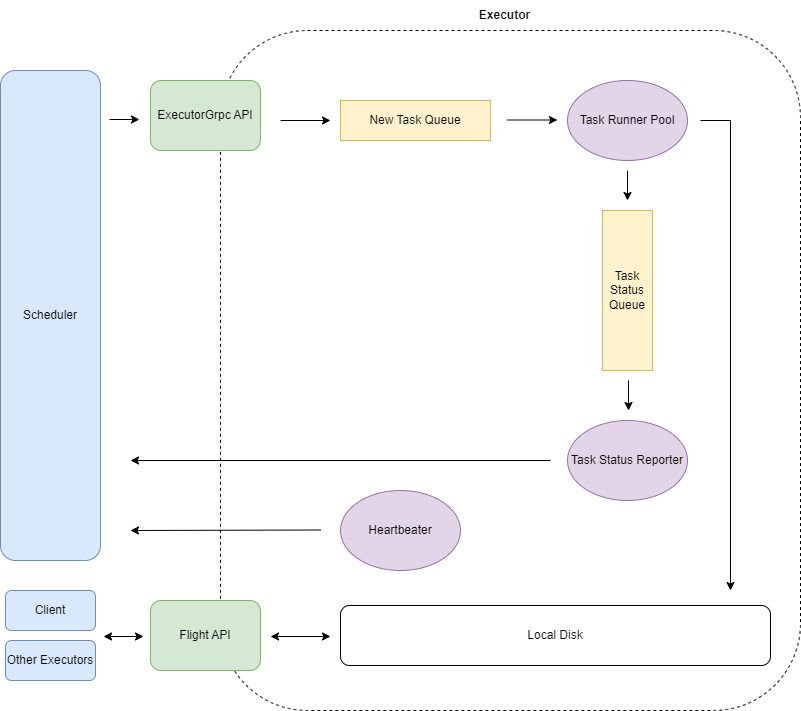
Executor 节点启动时
- 启动 ExecutorGrpc 服务,负责接收 Scheduler 节点发送的任务和其他指令
- 启动 Flight 服务,Client 和其他 Executor 通过 Flight 协议读取本机执行结果数据
- 向 Scheduler 注册(id/ip/port、计算资源总量等)
- 启动心跳任务,定时向所有 Scheduler 节点发送心跳
- 启动任务执行池,负责轮询队列获取新任务并执行
- 启动执行状态上报任务,负责上报任务状态给 Scheduler
Executor 执行的基本单元是 Task,一个 Task 会执行一个 Job 内的一个 stage 对应的一个 partition。
pub struct TaskDefinition {
/// 在执行图中的唯一的(单调递增)
pub task_id: usize,
/// 所属 job
pub job_id: String,
/// 所属 stage
pub stage_id: usize,
/// partition
pub partition_id: usize,
/// stage 执行计划
pub plan: Arc<dyn ExecutionPlan>,
/// Scheduler 发起任务时间
pub launch_time: u64,
/// 所属会话
pub session_id: String,
/// 会话设置
pub props: Arc<HashMap<String, String>>,
}
Ballista 运行 CPU 密集型任务
Ballista 采用 Tokio 作为 Rust 异步运行时。Tokio 使用协作式调度,异步任务会在执行到 .await 时切换其他任务执行,使用 Tokio 须遵守 "Async code should never spend a long time without reaching an .await."(参考 Tokio maintainer 的这篇博客)。因此 CPU 密集型任务会长时间占用 CPU,导致运行时上的其他任务无法被及时执行(如心跳)。
Ballista 解决此问题的办法是
- 采用单独的运行时专门跑 CPU 密集型任务
- IO 密集型任务运行时与 CPU 密集型任务运行时通过队列通信(创新新任务/任务执行结果通知)
- 当然 CPU 密集型任务代码仍要遵守
"Async code should never spend a long time without reaching an .await."
更多细节可参考 Datafusion maintainer 的这篇文章:https://thenewstack.io/using-rustlangs-async-tokio-runtime-for-cpu-bound-tasks/ 。